Projects
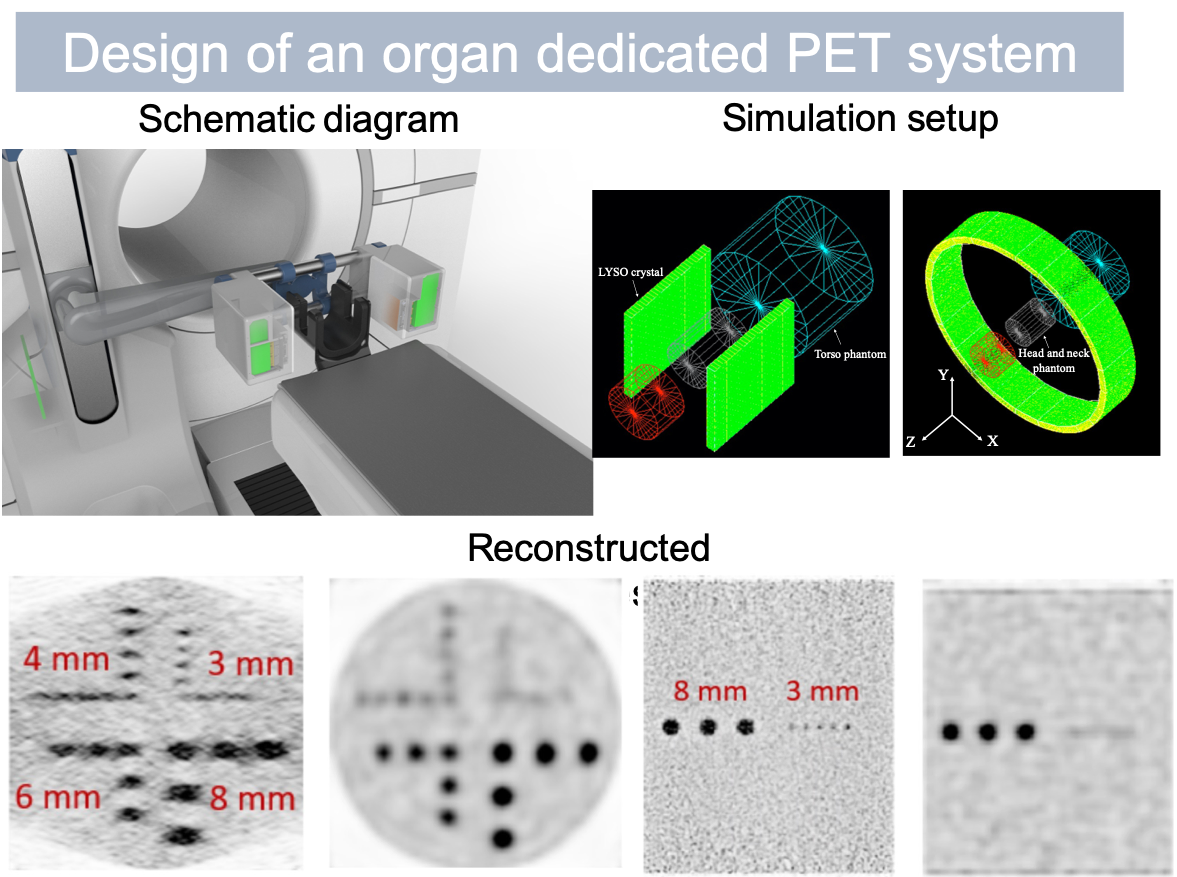
Design study of an organ dedicated PET system
Organ dedicated PET system can improve the spatial resolution and photon sensitivity in an organ-specific imaging environment compared with whole-body PET. Head and neck cancer needs high-resolution imaging due to its complex anatomy and vital physiological role. A dedicated PET system was evaluated and compared with GE Discovery MI. The results showed that the dedicated system could achieve a better performance in terms of noise equivalent count rate, photon sensitivity, spatial resolution, and lesion visualization capability. A PET system will be built based on this design.
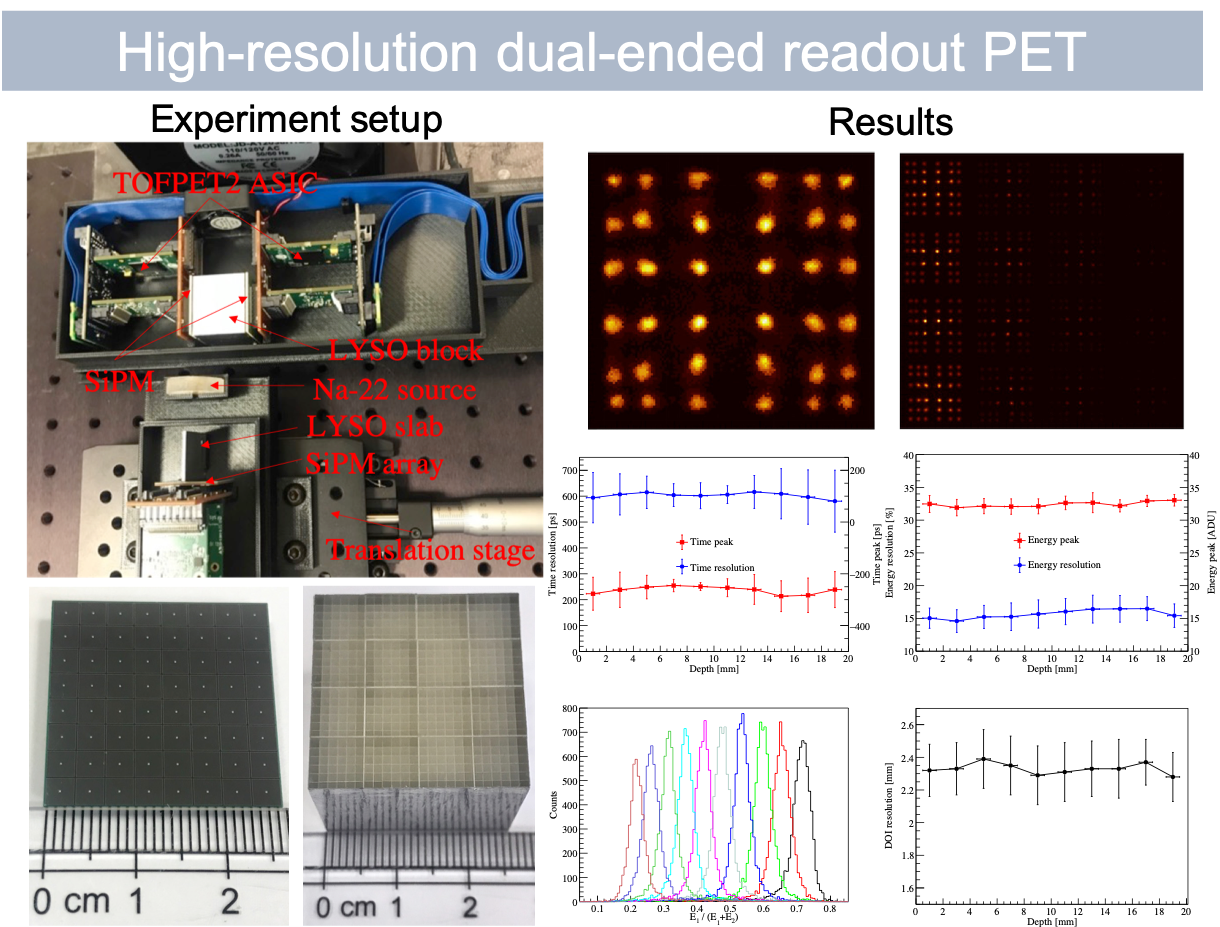
Design and characterization of a dual-ended readout PET detector
Depth-of-interaction (DOI) capability is important for achieving high spatial resolution and photon sensitivity in an organ dedicated PET system, and dual-ended readout can achieve good DOI resolution. The LYSO block contained 4×4 LYSO unit, each LYSO unit contained 6×6 LYSO crystal, and the crystal size was 1×1×20 mm³. The LYSO block was readout by two SiPM from both sides. The energy, coincidence time and DOI resolution were measured as 15.7±0.7%, 602.1±10.6 ps, 2.33±0.07 mm respectively. The good DOI resolution indicates the potential of utilizing the detector for high-resolution PET applications.[paper]
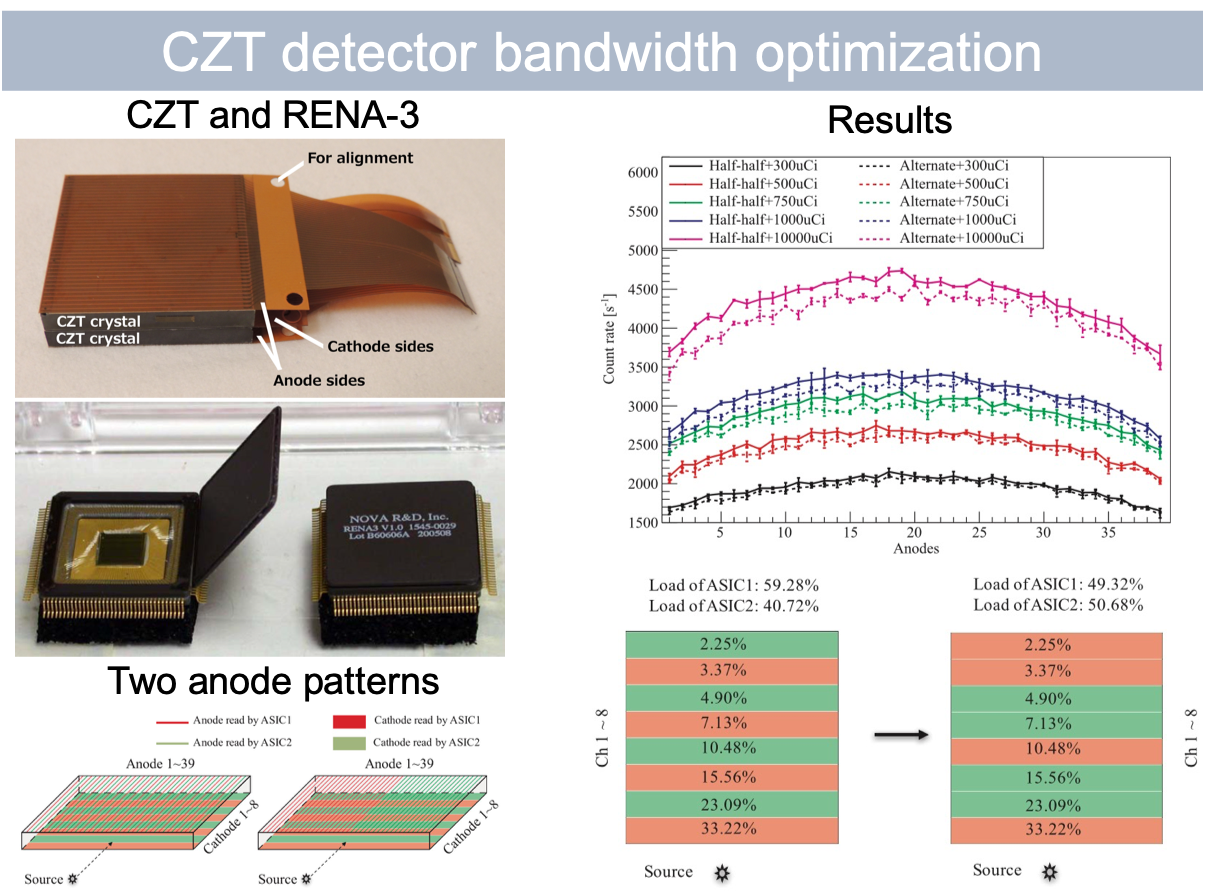
Influence of channel configuration on bandwidth of cadmium zinc telluride detector with a cross-strip pattern
Cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) detectors have superior spatial and energy resolution and have the potential to be used for positron emission tomography applications. The goal of this project is to improve the bandwidth of a cross-strip CZT detector, which has 39 anodes and 8 cathodes and needs two RENA-3 ASIC to readout its signal. I simulated the detector response in GATE and wrote a program to mimic the detector response and ASIC performance, taking Compton scattering and charge sharing into consideration. My work shows that a half-half anode pattern had a larger bandwidth than an alternate anode pattern and the cathode pattern could be further optimized based on the load. [paper]
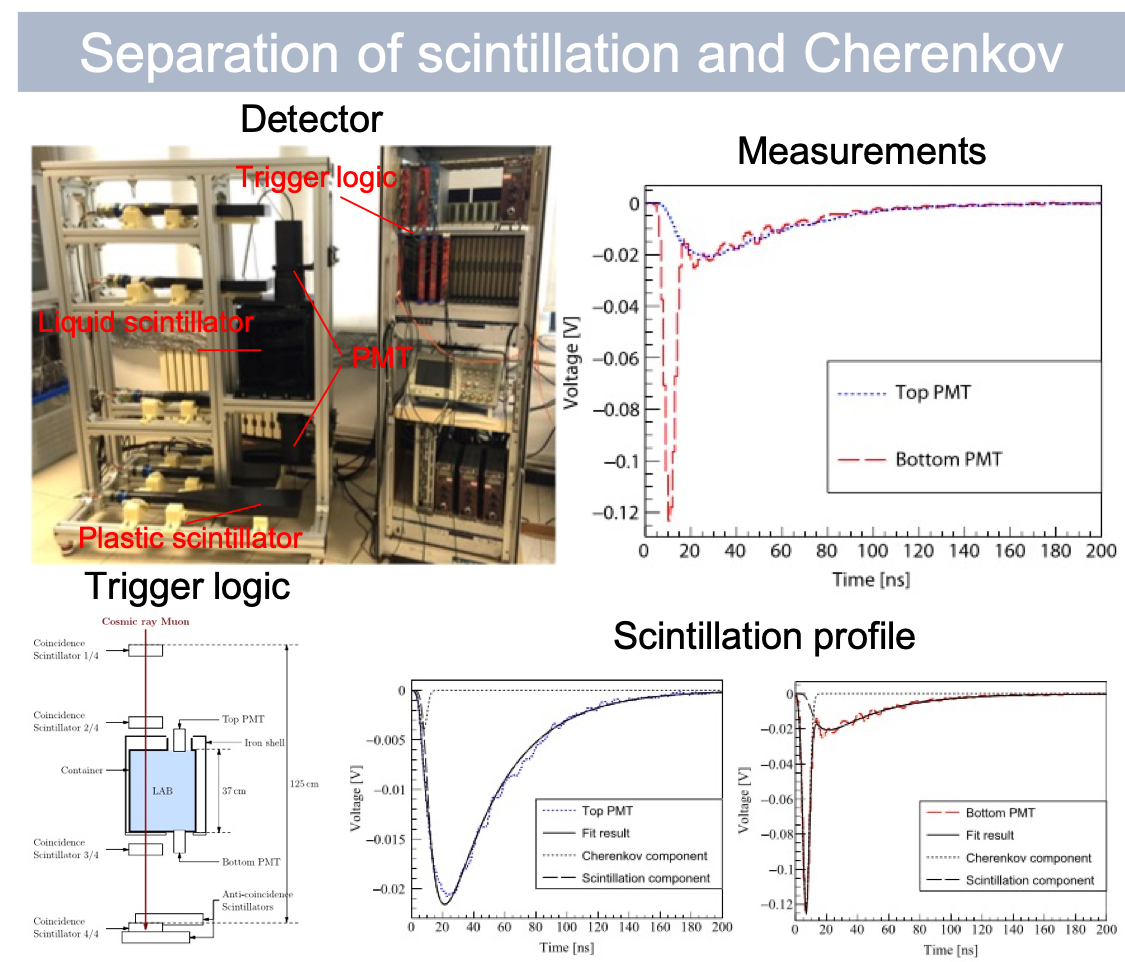
Separation of scintillation and Cherenkov lights in linear alkyl benzene
Water-based liquid scintillator (WbLS) is a promising detecting material for the next generation of neutrino and proton decay experiments. The purpose of this project is to verify the separable measurement of the simultaneous scintillation and Cherenkov lights in linear alkylbenzene (LAB), which is an important component of WbLS. The trigger signals and LAB lights were detected by photomultiplier tubes and digitized by an FADC CAEN VX1721. I wrote a real-time data streaming pipeline based on MIDAS, and designed a waveform-screening algorithm for data selection. The average time spectra of scintillation and Cherenkov lights were fitted by a biexponential function convoluted with a Gaussian detector response to get the rising and decay constants and light yield of scintillation light of LAB. The result is essential for guiding the making of WbLS. [paper]
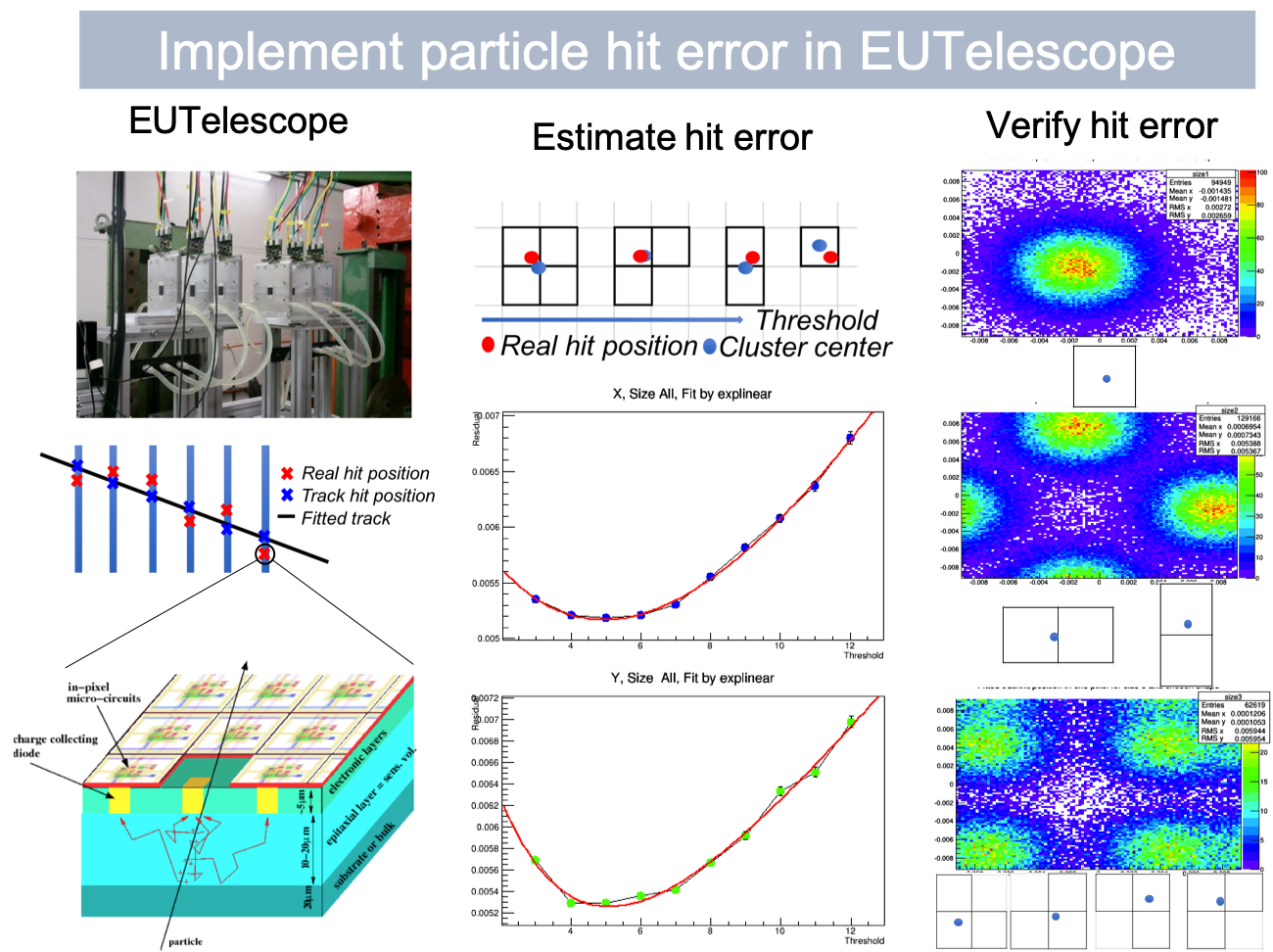
Implement particle hit errors to the EUTelescope data analysis platform
One primary goal of EUTelescope is to reconstruct particle tracks, whose accuracy depends on the particle hit error. The goal of the project is to estimate the particle hit error. I put forward physical models to describe the dependence of the particle hit error on the pixel activation thresholds and cluster shape, and verified the models by checking the particle hit distribution of different cluster shapes. The model was implemented in the EUTelescope data analysis platform. My work improves the particle hit error in low and middle thresholds, which is important for reducing the error of the reconstructed particle track.
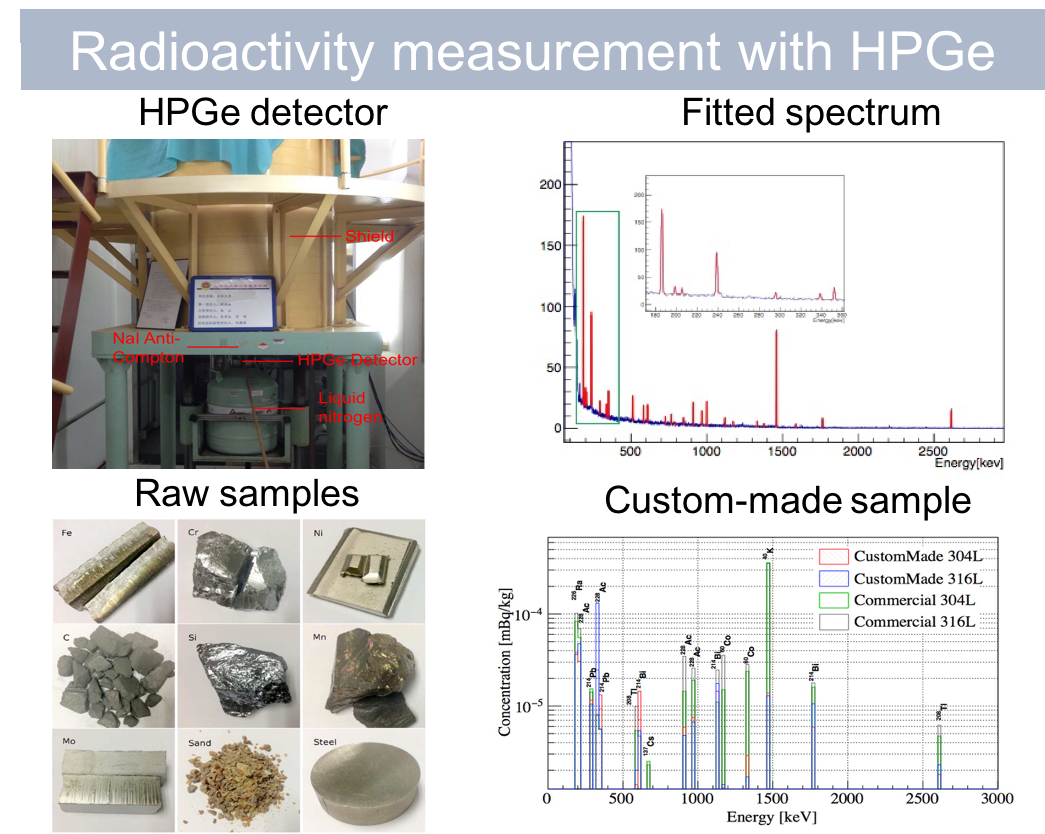
Assay of low-background stainless steel by smelting for the neutrino experiment at Jinping
It is important to control the background radioactivity in Jinping Underground Neutrino Experiment. The goal of this project is to smelt low-radioactivity stainless steel (SST) that is compatible with the ultra-low background requirement. A high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector was used to measure the radioactivity of raw materials and commercial samples of SST. I wrote a program to automatically identify radionuclide type and compute its radioactivity. My work helps to identify contamination sources such as C and Si and promotes to the smelting of custom-made SST samples, whose radioactivity is comparable to those used in other neutrino experiments such as Borexino and NEXT. [paper]